1. Summary
The sign of the arrival of the multimedia era is the popularity of sound cards, and the sign of the maturity of film is the appearance of sound films. All these show that the importance of sound to everyone is no less than any other information form. Audio format is the format for encoding and decoding sound files. There are currently two types of mainstream audio formats, lossy audio formats, such as MP3 format, and lossless audio formats, such as WAV. We often encounter situations where audio files cannot be played. This article will introduce commonly used audio formats and what to do if they are damaged.
2. Introduction of common audio formats
Common audio formats include MP3, AAC, AMR, WAV, OGG, M4A, etc.
1) MP3 audio format
The MP3 format is widely used, and the main application scenarios are music files, recording files, etc. The MP3 file structure is roughly divided into three parts: TAG_V2 (ID3V2), Frame, TAG_V1 (ID3V1).
|
ID3V2(file header)
|
Contains information such as author, composer, album, etc., and the length is not fixed, which expands the amount of information of ID3V1 |
|
Frame(middle of file) |
A series of frames, the number is determined by the file size and frame length The length of each FRAME may not be fixed, or it may be fixed, depending on the bitrate Each FRAME is divided into two parts: frame header and data entity The frame header records the bit rate, sampling rate, version and other information of mp3, and each frame is independent of each other |
|
ID3V1(end of file) |
Contains the author, composer, album and other information, the length is 128 BYTE |
The two parts ID3V2 and ID3V1 can be omitted, and it does not affect the playback of files, such as recording files. Since each data frame of MP3 has decoding information, and each frame is independent of each other, its decoding can start from any position.
2) AAC audio format
AAC is a new generation of audio lossy compression format, launched in 1997, the purpose is to replace the MP3 format, with a higher compression ratio. The audio file format of AAC is divided into ADIF and ADTS:
ADIF: Audio Data Interchange Format. The feature of this format is that the start of the audio data can be found deterministically, without the need to start decoding in the middle of the audio data stream, that is, its decoding must be carried out at the clearly defined start. Therefore, this format is commonly used in disk files.
The ADIF format of AAC is shown in the figure below:
|
Header |
Raw_data_stream |
ADTS: Audio Data Transport Stream. The characteristic of this format is that it is a bit stream with synchronization words, and decoding can start at any position in the stream. Its characteristics are similar to the mp3 data stream format.
The general format of AAC's ADTS is shown in the figure below:
|
|
Syncword |
Header |
Error_check |
Raw_data_block |
|
The figure shows the concise structure of one frame of ADTS, and the blank rectangles on both sides represent the data before and after one frame.
3) AMR audio format
AMR, the full name is: Adaptive Multi-Rate, is an audio coding file format, dedicated to effectively compress voice frequency. AMR audio is mainly used for audio compression of mobile devices. The compression ratio is very high, but the sound quality is relatively poor. It is mainly used for voice audio compression and is not suitable for the compression of music audio with high sound quality requirements. Mainly used for call recording, law enforcement recorder, social media app voice recording, etc.
The format of the AMR file is as follows:
|
Header |
Frame1 |
Frame2 |
… |
The frame format is as follows:
|
Header |
Raw_data_block |
The AMR format is similar to the MP3 format. Also, every frame has a frame header. The frame header contains synchronization information and decoding information. However, common players need the file header to recognize and play AMR audio files. In the case of a file header, arbitrary interception of the file does not affect playback.
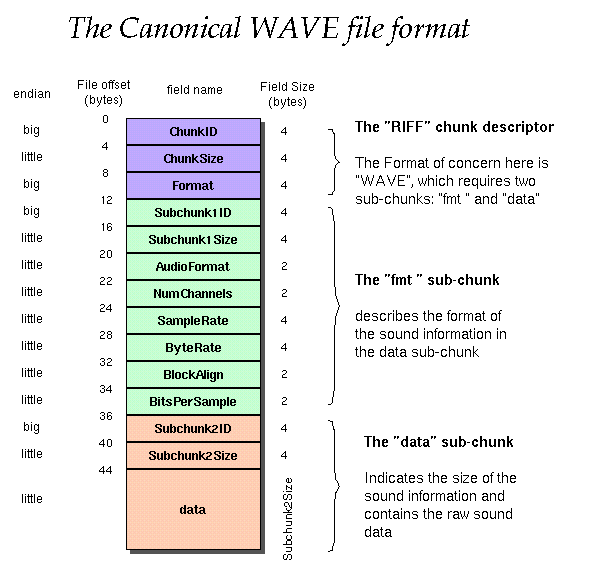
4) WAV audio format
WAV is an audio format developed by Microsoft. WAV conforms to the PIFF Resource Interchange File Format specification. The WAV file itself is composed of three "blocks" of information: the RIFF block that identifies the file as a WAV file, the FORMAT block that identifies parameters such as sampling rate, and the DATA block that contains actual data (samples). The WAV file format is as follows:
5) OGG audio format
Ogg is a free and open standard container format maintained by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The Ogg format is not restricted by software patents and is designed to efficiently stream media and process high-quality digital multimedia.
OGG organizes and links logical flows in units of pages, and each page has pageheader and pagedata. As shown in Figure 1 below:
|
PAGE1 |
PAGE2 |
PAGE3 |
… |
Each page is independent of each other and contains its own information. The size of the page is variable, usually 4K-8KB, and the maximum value cannot exceed 65307 bytes. The first two pages of the Ogg audio file contain audio decoding information.
|
OggS(Mark 4B) |
|||
|
Version(1B) |
Header_type(1B) |
|
|
|
Granule_position(8B) |
|||
|
|
Serial_number(4B)) |
||
|
|
Page_sequence(4B) |
||
|
|
CRC_checksum(4B) |
||
|
|
Num_segment (1B) |
Segment_table |
|
|
…… |
|||
|
Data |
|||
According to the introduction of various audio formats above, we can divide these audio formats into two categories:
1) The audio format of the decoded information in the header of each data frame.
Mainly include ADTS format of AMR, MP3, AAC. For this type of audio file, the header of each data frame contains the information needed to decode the audio. It has stream characteristics and is more suitable for the transmission and processing of audio streams. It can be played in any frame, that is, a piece of data can be intercepted at any position of the audio file and saved as a separate file for playback. You can do an experiment:
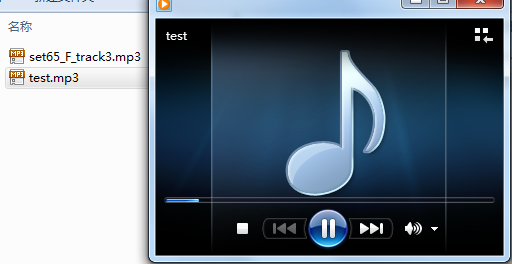
a. Select an MP3 file that can be played normally, as shown in the figure below:
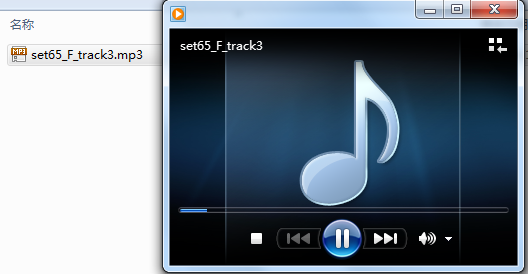
b. Use WINHEX to open the file, intercept a piece of data from any location, and save it as a new file. Name it test.mp3.
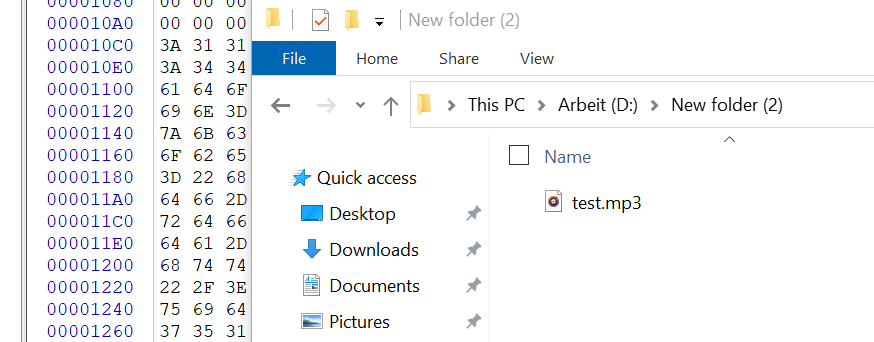
c. Play the test.mp3 file and find that it can be played normally.
2)
The audio format of the decoded information in the file header.
Mainly
include WAV, OGG, M4A, AAC ADIF format. For this type of audio file, the audio
decoding information is in the file header, that is, the beginning of the
decoding must be clearly defined. Do the same as an experiment:
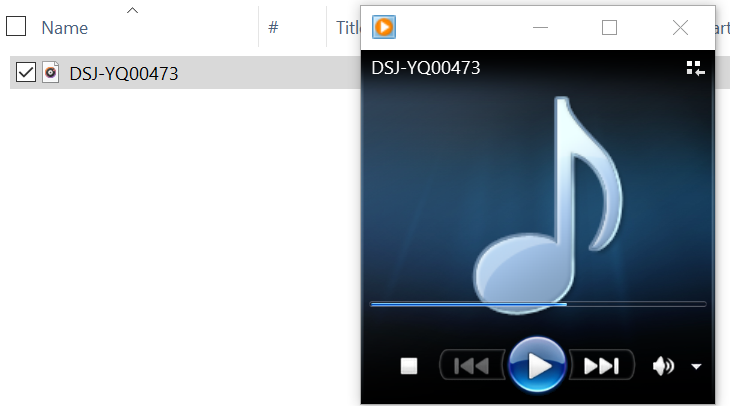
b. Open the file with winhex, fill in the header information with 0, and save the file.
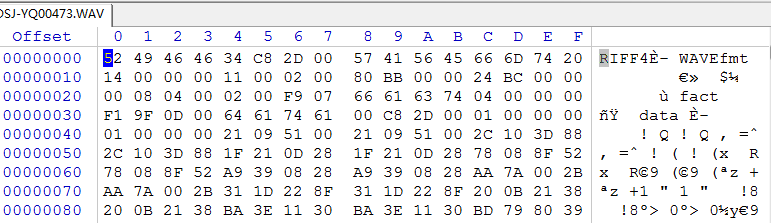
Before the head is cleared
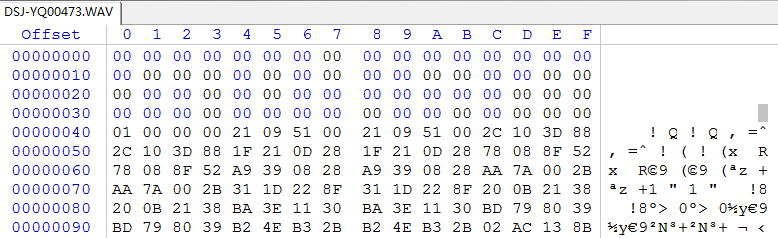
After the head is cleared
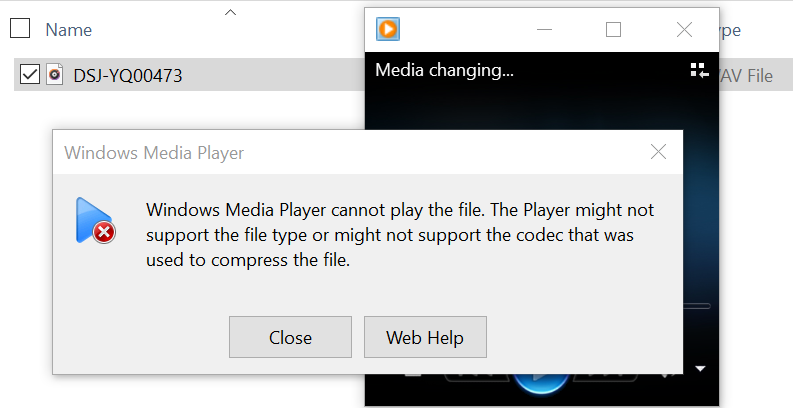
c. Play the test.wav file and find that it cannot be played.
3.
what caused the damage
We
often encounter audio files that cannot be played in our daily life. What will
cause the audio files to be unplayable?
1)
Sudden power failure caused the decoding information of the audio being
recorded to not be filled in completely or the file size information is
incorrect.
2)
After deleting the file by mistake and then writing to the disk, the file may
be overwritten. The audio file recovered by third-party software
3)
The virus causes part of the audio file to be encrypted.
4.
What should I do if it is damaged?
According
to the previous audio format introduction, we can conclude that for each frame
with decoded information format, you can start playing from any position of the
file, but if the header of the file is covered by a large amount of junk data,
the player cannot find it. When it reaches a valid audio frame and cannot be
played, what we have to do to restore this type of file is to extract the
uncovered part of the frame and save it as a new file. The audio repair
function of Meiya Pico Recovery Master uses this principle to achieve the
purpose of repairing audio files, that is, recovering audio files from damaged
files, extracting audio data from files such as image files. .